 | |
Throughout
history, the burning of biomass (fuel wood and animal waste) has been a major
source of energy in the world. This
process provides 15% of all energy consumed worldwide.
Biomass is an important form of alternate energy because it acts as a
middle source between our complete dependence on the unrenewable resources known
as fossil fuels, and the completely clean and environmentally benign energy
sources such as wind, solar, ocean, and hydropower.
There are three sources of biomass energy, wastes, standing forests, and
energy crops.
Wastes: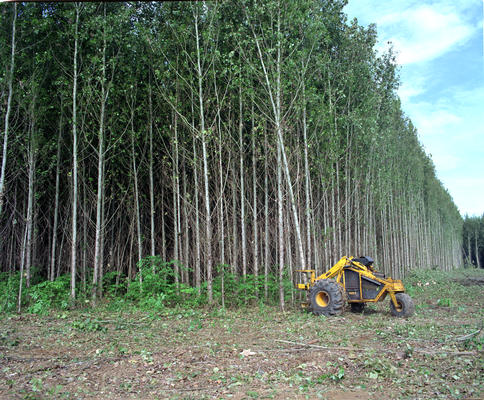
 |
wood scraps |
 |
unusable parts
of trees |
 |
pulp residue |
 |
paper scraps |
 |
municipal
solid wastes |
Standing
Forests:
 |
trees |
Energy
Crops:
 |
fast growing trees,
grasses, and other crops raised on large energy farms specifically for
energy. |
There are three
different technologies involved in extracting energy from biomass.
They are:
Direct Buring
 |
Using heat
produced after burning biomass. Direct
combustion is the oldest form of biomass energy and is effective if
practiced carefully. This
method of creating biomass fuel is fairly inexpensive as opposed to others. |
Thermochemical
 |
Converts
biomass into fuel, by ways of combustion without oxygen, which can be
substituted for petroleum and natural gas. The two best known product are syngas and methanol.
This form of conversion may release harmful pollutants into the
environment. |
Biochemical
 |
Converts
biomass into fuel by way of harnessing microorganisms to carry out the
conversion. This way of
conversion can be utilized in many ways.
It can produce ethanol for the base of the entire alcohol industry,
or it can be used as a fuel source. |
Advantages:
 |
Renewable
resource |
 |
Large source
of biomass energy |
 |
Energy farms
result in little erosion |
Disadvantages:
 |
Although
renewable, still causes environmental degradation. |
 |
Deprives soil
of nutrients, reducing fertility |
 |
Over
de-forestation |
 |
Inefficient
- over 3-10 times more energy may be used than is needed |
 |
Energy Farms
will eventually suffer from soul erosion, massive pesticide, herbicide, and
fertilizer
use. |
 |
Contributes to
the greenhouse effect when done unsustainably. |
|
